在 React 中悬停时添加一个类
Add a Class on hover in React
在 React 中添加悬停类:
- 在元素上设置
onMouseOver和道具。onMouseOut - 跟踪用户是否将鼠标悬停在状态变量中的元素上。
- 根据状态变量有条件地添加类。
应用程序.js
import './App.css'; import {useState} from 'react'; const App = () => { const [isHovering, setIsHovering] = useState(false); const handleMouseOver = () => { setIsHovering(true); }; const handleMouseOut = () => { setIsHovering(false); }; return ( <div> <div> <div className={isHovering ? 'bg-salmon' : ''} onMouseOver={handleMouseOver} onMouseOut={handleMouseOut} > Hover me </div> </div> </div> ); }; export default App;
这是App.css示例的文件。
应用程序.css
.bg-salmon { background-color: salmon; color: white; }
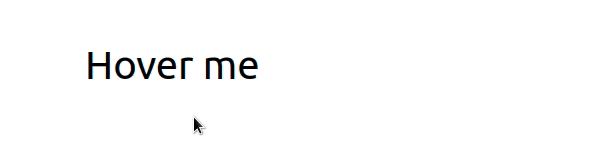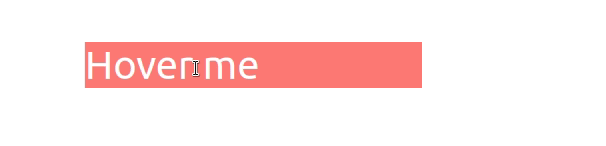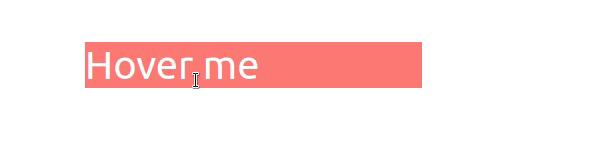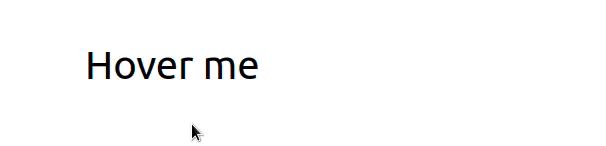
我们onMouseOver在元素上设置了 prop div,所以每次用户将鼠标悬停在元素上时,handleMouseOver都会调用该函数。
当
用户将光标移动到元素或其子元素之一时,将触发mouseover事件。
在我们的handleMouseOver函数中,我们只需将isHovering状态变量设置为true。
相反,在我们的handleMouseOut函数中,我们将state变量设置为
false.
当
用户的光标不再包含在元素或其子元素之一中时,将触发mouseout事件。
我们使用
三元运算符
有条件地将类添加到元素中。
应用程序.js
<div className={isHovering ? 'bg-salmon' : ''} onMouseOver={handleMouseOver} onMouseOut={handleMouseOut} > Hover me </div>
if/else三元运算符与语句非常相似。
它检查问号左边的值是否为真,如果是,运算符返回冒号左边的值,否则返回右边的值。
换句话说,如果isHovering变量存储一个true值,我们将
bg-salmon类添加到元素,否则返回一个空字符串。
当用户将鼠标悬停在div元素上时:
handleMouseOver函数被调用。isHovering状态变量设置true为。- 该类被添加到元素中。
相反,当用户将光标移出div元素时:
handleMouseOut函数被调用。isHovering状态变量设置false为。- 该类不会添加到元素中。
