在 Python 中验证用户输入的字符串
Validating user input string in Python
要验证字符串用户输入值:
- 使用
while循环迭代,直到提供的值有效。 - 在每次迭代中,检查提供的字符串是否满足条件。
- 如果满足条件,则跳出循环。
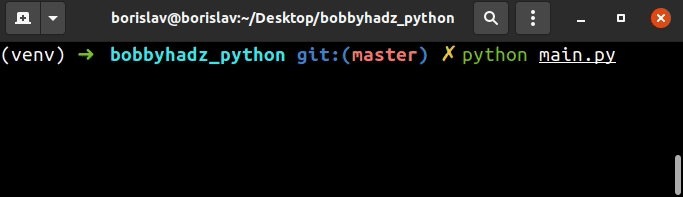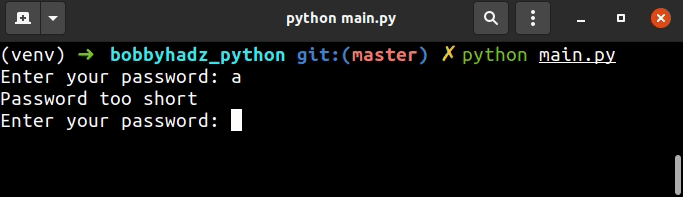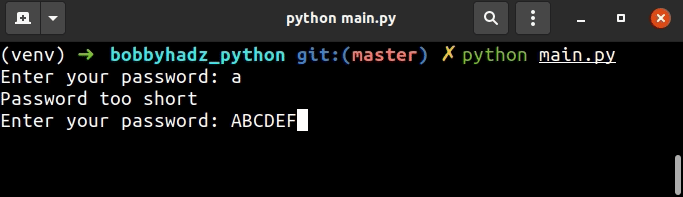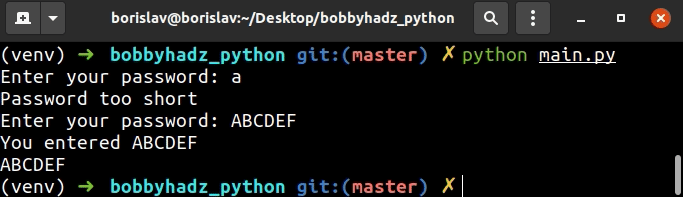
主程序
options = ['a', 'b', 'c'] user_input = '' while user_input.lower() not in options: user_input = input('Enter a, b or c: ') print(user_input) # ---------------------------------------- # 👇️ check if user input string is at least 5 characters long password = '' while True: password = input('Enter your password: ') if len(password) < 5: print('Password too short') continue else: print(f'You entered {password}') break print(password)
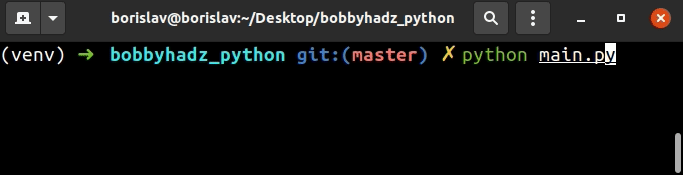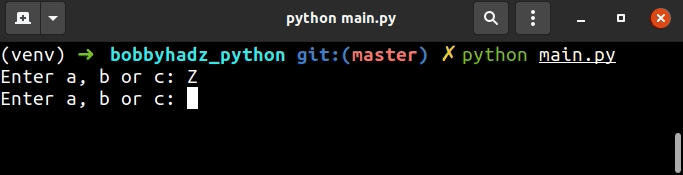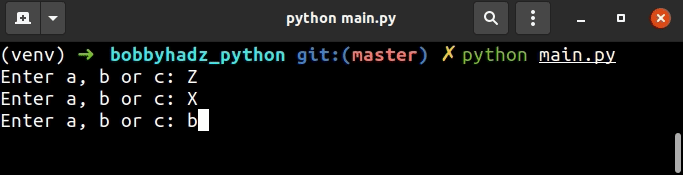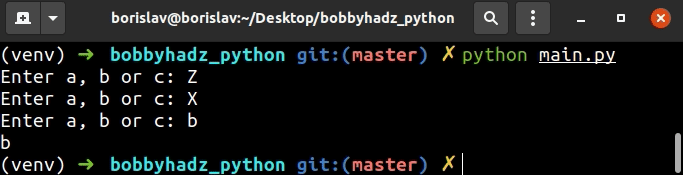
第一个示例检查提供的用户输入字符串是否是列表中的一项。
循环不断提示用户,while直到提供的值是选项之一。
主程序
options = ['a', 'b', 'c'] user_input = '' while user_input.lower() not in options: user_input = input('Enter a, b or c: ') print(user_input)
如果提供的值是选项之一,while则不再满足循环中的条件,我们将跳出循环。
您还可以使用while True带有break语句的循环来验证字符串输入值。
主程序
password = '' while True: password = input('Enter your password: ') if len(password) < 5: print('Password too short') continue else: print(f'You entered {password}') break print(password)
我们使用了一个while True循环来提示用户输入。
如果用户输入的值少于 5 个字符,我们将使用该
continue语句再次提示用户。
该continue语句继续循环的下一次迭代。
否则,该else块将在我们打印用户输入的值并跳出循环的地方运行。
break
语句跳出最内层的封闭或
for循环while。
验证字符串输入值时,您可能希望在将输入值与其他字符串进行比较时使用str.lower()或
str.upper()方法将输入值小写或大写。
主程序
print('HELLO'.lower()) # 👉️ 'hello' print('hello'.upper()) # 👉️ 'HELLO'
