目录
AttributeError: ‘str’ object has no attribute in Python
- AttributeError: ‘str’ 对象没有属性 ‘X’
- AttributeError: ‘str’ 对象没有属性 ‘ITEMS’ 或 ‘KEYS’
- AttributeError: ‘str’ 对象没有属性 ‘CONTAINS’
- AttributeError: ‘str’ 对象没有属性 ‘WRITE’
- AttributeError: ‘str’ 对象没有属性 ‘READ’
- AttributeError: ‘str’ 对象没有属性 ‘REMOVE’
AttributeError: ‘str’ 对象在 Python 中没有属性 ‘X’
当我们尝试访问字符串对象上不存在的属性时,会出现 Python“AttributeError: ‘str’ object has no attribute”。
要解决该错误,请在访问属性之前确保该值属于预期类型。
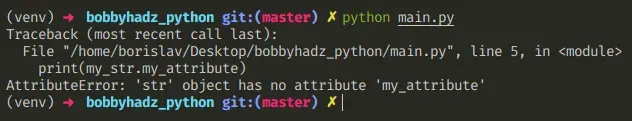
下面是错误如何发生的示例。
my_str = 'bobbyhadz.com' # ⛔️ AttributeError: 'str' object has no attribute 'my_attribute' print(my_str.my_attribute)
我们试图访问字符串对象上不存在的属性并收到错误。
如果您print()您正在访问属性的值,它将是一个字符串。
要解决该错误,请查明您在代码中将值设置为字符串的确切位置并更正分配。
在字符串上调用该decode()方法会导致错误
错误的一个常见原因是试图
在字符串(已解码)对象上调用该decode()方法
。
my_str = 'bobbyhadz.com' # ⛔️ AttributeError: 'str' object has no attribute decoded = my_str.decode(enoding='utf-8')
要解决该错误,请删除对该decode()方法的调用,因为如果您有一个字符串,它已经被解码了。
该decode()方法用于将字节对象解码为字符串。
在调用列表方法之前访问特定索引处的列表
在调用列表方法之前,请确保您没有访问特定索引处的列表。
my_list = ['bobby', 'hadz', '.'] # ⛔️ AttributeError: 'str' object has no attribute my_list[2].append('com')
我们访问了 index 处的列表元素2,它是一个字符串,并调用了
append()导致错误的字符串上的方法。
要解决错误,我们必须调用append()列表中的方法。
my_list = ['bobby', 'hadz', '.'] my_list.append('com') print(my_list) # 👉️ ['bobby', 'hadz', '.', 'com']
将变量重新分配给字符串
确保您没有将变量重新分配给代码中某处的字符串。
my_list = ['bobby', 'hadz', '.'] # 👇️ list got reassigned to a string my_list = 'hello world' # ⛔️ AttributeError: 'str' object has no attribute my_list.append('com')
我们最初将变量的值设置my_list为列表,但后来我们将其设置为导致错误的字符串。
在文件名上调用writeor方法read
如果您正在写入或读取文件,请确保您没有调用
文件名上的write()或方法。read()
file_name = 'example.txt' with open(file_name, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as my_file: # ⛔️ AttributeError: 'str' object has no attribute file_name.write('first line' + '\n') file_name.write('second line' + '\n') file_name.write('third line' + '\n')
write()代码示例中的问题是我们在字符串(文件名)上调用方法,而我们应该在文件对象上调用它。
file_name = 'example.txt' with open(file_name, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as my_file: my_file.write('first line' + '\n') my_file.write('second line' + '\n') my_file.write('third line' + '\n')
检查字符串是否包含子字符串
如果需要检查子字符串是否在字符串中,请使用in运算符。
my_string = 'bobbyhadz.com' if '.com' in my_string: # 👇️ this runs print('string contains substring') else: print('string does NOT contain substring')
如果子字符串包含在字符串中,则运算符返回,
否则in返回。TrueFalse
如果您需要以不区分大小写的方式检查字符串是否包含子字符串,请将两个字符串都转换为小写。
my_string = 'BOBBYHADZ.COM' substring = '.com' if substring.lower() in my_string.lower(): # 👇️ this runs print('string contains substring') else: print('string does NOT contain substring')
将两个字符串转换为相同的大小写允许进行不区分大小写的成员资格测试。
检查对象是否包含属性
如果需要检查对象是否包含属性,请使用该hasattr
函数。
my_string = 'bobbyhadz.com' if hasattr(my_string, 'upper'): print(my_string.upper()) # 👉️ BOBBYHADZ.COM else: print('Attribute is not present in object')
hasattr函数
采用以下 2 个参数:
| 姓名 | 描述 |
|---|---|
object |
我们要测试属性是否存在的对象 |
name |
对象中要检查的属性的名称 |
如果字符串是对象属性之一的名称,则hasattr()函数返回,否则返回。TrueFalse
hasattr如果该属性在对象上不存在,则使用该函数将处理错误,但是,您仍然必须弄清楚在代码中为变量分配字符串的位置。找出变量在哪里分配了一个字符串
开始调试的一个好方法是print(dir(your_object))查看字符串具有哪些属性。
这是打印 a 的属性的示例string。
my_string = 'hello world' # [ 'capitalize', 'casefold', 'center', 'count', 'encode', 'endswith', 'expandtabs', 'find', 'format', # 'format_map', 'index', 'isalnum', 'isalpha', 'isascii', 'isdecimal', 'isdigit', 'isidentifier', # 'islower', 'isnumeric', 'isprintable', 'isspace', 'istitle', 'isupper', 'join', 'ljust', 'lower', # 'lstrip', 'maketrans', 'partition', 'removeprefix', 'removesuffix', 'replace', 'rfind', 'rindex', # 'rjust', 'rpartition', 'rsplit', 'rstrip', 'split', 'splitlines', 'startswith', 'strip', 'swapcase', # 'title', 'translate', 'upper', 'zfill'] print(dir(my_string))
如果将一个类传递给dir()
函数,它会返回该类属性的名称列表,并递归地返回其基类的属性。
要解决该错误,请在访问属性之前将值转换为正确的类型,或者在访问任何属性之前更正分配给变量的值的类型。
确保:
- 您没有拼错对象上存在的方法或属性
str。 - 您没有将字符串分配给应该存储不同值的变量。
- 您不会尝试调用
decode()已存储字符串的变量。
针对特定方法解决错误的例子
以下是针对特定方法解决错误的一些示例。单击链接导航到副标题。
- AttributeError: ‘str’ 对象没有属性 ‘items’ 或 ‘keys’
- AttributeError: ‘str’ 对象没有属性 ‘contains’
- AttributeError: ‘str’ 对象没有属性 ‘write’
- AttributeError: ‘str’ 对象没有属性 ‘read’
- AttributeError: ‘str’ 对象没有属性 ‘remove’
- AttributeError: ‘str’ 对象没有属性 ‘append’
- AttributeError: ‘str’ 对象没有属性 ‘decode’
- AttributeError: ‘str’ 对象没有属性 ‘get’ (Python)
- AttributeError: ‘str’ 对象没有属性 ‘strftime’
AttributeError: ‘str’ 对象没有属性 ‘items’ 或 ‘keys’
Python AttributeError: ‘str’ object has no attribute ‘items’ or ‘keys’ 当我们尝试在字符串而不是字典上调用items()or方法时发生。keys()
要解决该错误,请确保解析字符串(如果您有 JSON 字符串)或更正分配并调用items()or keys()on a dict。
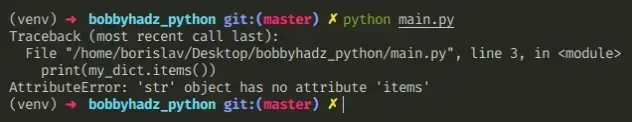
下面是错误如何发生的示例。
# 👇️ this is a string my_dict = '{"name": "Bobby Hadz", "age": 30}' # ⛔️ AttributeError: 'str' object has no attribute 'items' print(my_dict.items()) # ⛔️ AttributeError: 'str' object has no attribute 'keys' print(my_dict.keys())
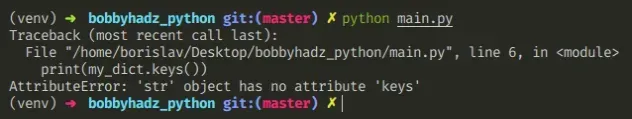
我们试图在字符串上调用items()和keys()方法并得到错误。
如果您有 JSON 字符串,请使用该json.loads()方法将其解析为本机 Python 字典。
import json my_dict = '{"name": "Bobby Hadz", "age": 30}' # 👇️ parse JSON string to native Python dict parsed = json.loads(my_dict) # 👇️ dict_items([('name', 'Bobby Hadz'), ('age', 30)]) print(parsed.items()) # 👇️ dict_keys(['name', 'age']) print(parsed.keys())
在调用和方法之前,我们使用该json.loads()方法将 JSON 字符串解析为 Python 字典。items()keys()
items()
如果您需要在调用or方法之前检查该值是否为字典keys(),请使用该isinstance函数。
my_dict = {"name": "Bobby Hadz", "age": 30} if isinstance(my_dict, dict): # 👇️ dict_items([('name', 'Bobby Hadz'), ('age', 30)]) print(my_dict.items())
如果传入的对象是传入类的实例或子类,则isinstance函数返回
。True
如果您发出 HTTP 请求,请确保您没有将headers
字典转换为 JSON。
import requests def make_request(): res = requests.post( 'https://reqres.in/api/users', data={'name': 'Bobby Hadz', 'job': 'programmer'}, # 👇️ should be a Python dictionary (NOT json str) headers={'Accept': 'application/json', 'Content-Type': 'application/json'} ) print(res.json()) # parse JSON response to native Python object make_request()
关键字headers参数应该是 Python 字典,而不是 JSON 字符串。
确保您没有json.dumps()在字典上调用该方法,因为那样会将其转换为 JSON 字符串。
import json my_dict = {"name": "Bobby Hadz", "age": 30} print(type(my_dict)) # 👉️ <class 'dict'> # 👇️ json.dumps() converts a Python object to JSON string json_str = json.dumps(my_dict) print(type(json_str)) # 👉️ <class 'str'>
json.dumps方法将 Python 对象转换为 JSON 格式的字符串。
如果您有一个 JSON 字符串并试图将其解析为本机 Python 字典,请使用该json.loads()方法。
import json json_str = r'{"name": "Bobby Hadz", "age": 30}' my_dict = json.loads(json_str) print(type(my_dict)) # 👉️ <class 'dict'>
json.loads方法将 JSON 字符串解析为本机 Python 对象。
如果正在解析的数据不是有效的 JSON 字符串,JSONDecodeError则会引发 a 。
开始调试的一个好方法是print(dir(your_object))查看字符串具有哪些属性。
这是打印 a 的属性的示例string。
my_string = 'bobbyhadz.com' # [ 'capitalize', 'casefold', 'center', 'count', 'encode', 'endswith', 'expandtabs', 'find', 'format', # 'format_map', 'index', 'isalnum', 'isalpha', 'isascii', 'isdecimal', 'isdigit', 'isidentifier', # 'islower', 'isnumeric', 'isprintable', 'isspace', 'istitle', 'isupper', 'join', 'ljust', 'lower', # 'lstrip', 'maketrans', 'partition', 'removeprefix', 'removesuffix', 'replace', 'rfind', 'rindex', # 'rjust', 'rpartition', 'rsplit', 'rstrip', 'split', 'splitlines', 'startswith', 'strip', 'swapcase', # 'title', 'translate', 'upper', 'zfill'] print(dir(my_string))
如果将一个类传递给dir()
函数,它会返回该类属性的名称列表,并递归地返回其基类的属性。
由于items()和keys()不是字符串实现的方法,所以导致错误。
- AttributeError: ‘str’ 对象没有属性 ‘contains’
- AttributeError: ‘str’ 对象没有属性 ‘write’
- AttributeError: ‘str’ 对象没有属性 ‘read’
- AttributeError: ‘str’ 对象没有属性 ‘remove’
- AttributeError: ‘str’ 对象没有属性 ‘append’
- AttributeError: ‘str’ 对象没有属性 ‘decode’
- AttributeError: ‘str’ 对象没有属性 ‘get’ (Python)
- AttributeError: ‘str’ 对象没有属性 ‘strftime’
AttributeError: ‘str’ 对象没有属性 ‘contains’
contains()当我们尝试在字符串上调用方法时,会出现 Python“AttributeError: ‘str’ object has no attribute ‘contains’” 。
要解决错误,请使用in运算符,例如,'ab' in 'abc'因为字符串没有contains方法。
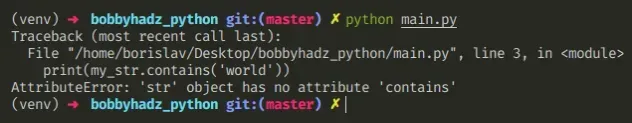
下面是错误如何发生的示例。
my_str = 'bobbyhadz.com' # ⛔️ AttributeError: 'str' object has no attribute 'contains' print(my_str.contains('com'))
我们试图contains()在字符串上调用该方法并收到错误,因为字符串没有方法contains。
您可以使用in运算符来检查字符串中是否包含子字符串。
my_str = 'bobbyhadz.com' if 'com' in my_str: print('substring is contained in string') # 👉️ this runs else: print('substring is NOT contained in string')
您还可以将逻辑提取到可重用函数中。
def contains(string, substring): return substring in string print(contains('bobbyhadz.com', 'com')) # 👉️ True print(contains('bobbyhadz.com', 'abc')) # 👉️ False
in 运算符测试成员资格。例如,如果是 的成员
,则x in s计算为,否则计算为。TruexsFalse
my_str = 'bobbyhadz.com' print('bobby' in my_str) # 👉️ True print('another' in my_str) # 👉️ False
检查字符串是否包含忽略大小写的子字符串
如果您需要检查字符串中是否包含忽略大小写的子字符串,请将两个字符串都转换为小写。
my_str = 'BOBBYHADZ.COM' my_substr = 'com' if my_substr.lower() in my_str.lower(): print('substring is in string') # 👉️ this runs else: print('substring is not in string')
我们将两个字符串都转换为小写,以便能够检查子字符串是否在忽略大小写的字符串中。
检查字符串是否不包含子字符串
如果您需要检查子字符串是否不在字符串中,请改用not in
运算符。
my_str = 'BOBBYHADZ.COM' if 'another' not in my_str: print('substring is NOT in string') # 👉️ this runs
xnot in返回ins的否定。xs
所有内置序列和集合类型都支持inandnot in运算符。
dict。请注意,空字符串始终被视为任何其他字符串的子字符串。
my_str = 'bobbyhadz.com' print('' in my_str) # 👉️ True
开始调试的一个好方法是print(dir(your_object))查看字符串具有哪些属性。
这是打印 a 的属性的示例string。
my_string = 'bobbyhadz.com' # [ 'capitalize', 'casefold', 'center', 'count', 'encode', 'endswith', 'expandtabs', 'find', 'format', # 'format_map', 'index', 'isalnum', 'isalpha', 'isascii', 'isdecimal', 'isdigit', 'isidentifier', # 'islower', 'isnumeric', 'isprintable', 'isspace', 'istitle', 'isupper', 'join', 'ljust', 'lower', # 'lstrip', 'maketrans', 'partition', 'removeprefix', 'removesuffix', 'replace', 'rfind', 'rindex', # 'rjust', 'rpartition', 'rsplit', 'rstrip', 'split', 'splitlines', 'startswith', 'strip', 'swapcase', # 'title', 'translate', 'upper', 'zfill'] print(dir(my_string))
如果将一个类传递给dir()
函数,它会返回该类属性的名称列表,并递归地返回其基类的属性。
由于contains()不是字符串实现的方法,所以报错。
- AttributeError: ‘str’ 对象没有属性 ‘write’
- AttributeError: ‘str’ 对象没有属性 ‘read’
- AttributeError: ‘str’ 对象没有属性 ‘remove’
- AttributeError: ‘str’ 对象没有属性 ‘append’
- AttributeError: ‘str’ 对象没有属性 ‘decode’
- AttributeError: ‘str’ 对象没有属性 ‘get’ (Python)
- AttributeError: ‘str’ 对象没有属性 ‘strftime’
AttributeError: ‘str’ 对象没有属性 ‘write’
Python“AttributeError: ‘str’ object has no attribute ‘write’” 发生在我们write()对字符串(例如文件名)而不是文件对象调用方法时。
要解决该错误,请write()在打开文件后调用文件对象上的方法。
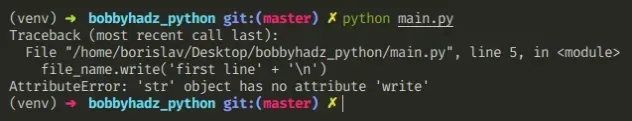
下面是错误如何发生的示例。
file_name = 'example.txt' with open(file_name, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as my_file: # ⛔️ AttributeError: 'str' object has no attribute 'write' file_name.write('first line' + '\n') file_name.write('second line' + '\n') file_name.write('third line' + '\n')
问题是我们write()在文件名上调用了方法,它是一个字符串。
相反,write()在打开文件对象后调用该方法。
file_name = 'example.txt' with open(file_name, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as my_file: # ✅ calling write() on file object my_file.write('first line' + '\n') my_file.write('second line' + '\n') my_file.write('third line' + '\n')
with open()语法负责自动关闭文件,即使抛出异常也是如此。
或者,您可以将文件对象存储到变量中并手动关闭它。
file_name = 'example.txt' my_file = open(file_name, 'w', encoding='utf-8') my_file.write('first line' + '\n') my_file.write('second line' + '\n') my_file.write('third line' + '\n') my_file.close()
请注意,最好使用with open()语法,因为它会在我们完成后自动关闭文件。
如果需要将数据附加到文件,请使用a标志而不是w.
file_name = 'example.txt' with open(file_name, 'a', encoding='utf-8') as my_file: my_file.write('first line' + '\n') my_file.write('second line' + '\n') my_file.write('third line' + '\n')
如果您需要从文件读取和写入文件,请使用该r+标志。
file_name = 'example.txt' with open(file_name, 'r+', encoding='utf-8') as my_file: read_data = my_file.read() print(read_data) my_file.write('first line' + '\n') my_file.write('second line' + '\n') my_file.write('third line' + '\n')
开始调试的一个好方法是print(dir(your_object))查看字符串具有哪些属性。
这是打印 a 的属性的示例string。
my_string = 'hello world' # [ 'capitalize', 'casefold', 'center', 'count', 'encode', 'endswith', 'expandtabs', 'find', 'format', # 'format_map', 'index', 'isalnum', 'isalpha', 'isascii', 'isdecimal', 'isdigit', 'isidentifier', # 'islower', 'isnumeric', 'isprintable', 'isspace', 'istitle', 'isupper', 'join', 'ljust', 'lower', # 'lstrip', 'maketrans', 'partition', 'removeprefix', 'removesuffix', 'replace', 'rfind', 'rindex', # 'rjust', 'rpartition', 'rsplit', 'rstrip', 'split', 'splitlines', 'startswith', 'strip', 'swapcase', # 'title', 'translate', 'upper', 'zfill'] print(dir(my_string))
如果将一个类传递给dir()
函数,它会返回该类属性的名称列表,并递归地返回其基类的属性。
由于该str对象未实现write()方法,因此导致错误。
- AttributeError: ‘str’ 对象没有属性 ‘read’
- AttributeError: ‘str’ 对象没有属性 ‘remove’
- AttributeError: ‘str’ 对象没有属性 ‘append’
- AttributeError: ‘str’ 对象没有属性 ‘decode’
- AttributeError: ‘str’ 对象没有属性 ‘get’ (Python)
- AttributeError: ‘str’ 对象没有属性 ‘strftime’
AttributeError: ‘str’ 对象没有属性 ‘read’
Python“AttributeError: ‘str’ object has no attribute ‘read’” 发生在我们read()在字符串(例如文件名)而不是文件对象上调用该方法或json.load()错误使用该方法时。
要解决该错误,请read()在打开文件后调用文件对象上的方法。
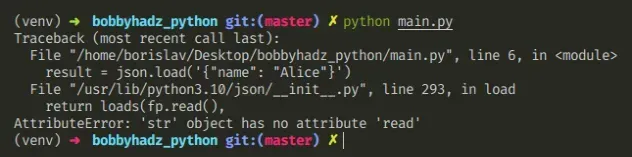
下面是错误如何发生的示例。
file_name = 'example.txt' with open(file_name, encoding='utf-8') as f: # ⛔️ AttributeError: 'str' object has no attribute 'read' read_data = file_name.read() print(read_data)
我们试着打电话给read()在文件名字符串而不是导致错误的文件对象上调用该方法。
如果您正在从文件中读取,请确保调用read()调用文件对象上的方法。
file_name = 'example.txt' with open(file_name, encoding='utf-8') as f: # ✅ calling read() on file object read_data = f.read() print(read_data)
错误的另一个常见原因是json.load()在尝试将 JSON 字符串解析为本机 Python 对象时使用该方法。
import json # ⛔️ AttributeError: 'str' object has no attribute 'read' result = json.load('{"name": "Alice"}')
json.load方法用于将文件反序列化为 Python 对象,而
json.loads方法用于将 JSON 字符串反序列化为 Python 对象。
如果您尝试将 JSON 字符串解析为本机 Python 对象,请改用
json.loads(with s) 方法。
import json result = json.loads('{"name": "Alice"}') print(type(result)) # 👉️ <class 'dict'> print(result) # 👉️ {'name': 'Alice'}
我们使用该方法将 JSON 字符串解析为字典json.loads()。
如果您尝试使用该json.load()方法将文件反序列化为 Python 对象,请打开文件并将文件对象传递给该json.load()
方法。
import json file_name = 'example.json' with open(file_name, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f: my_data = json.load(f) print(my_data) # 👉️ {'name': 'Alice', 'age': 30}
该json.load()方法需要一个包含实现方法的 JSON 文档的文本文件或二进制文件.read()。如果您使用json.load()
字符串调用该方法,它会尝试调用该read()字符串上的方法。
如果您在使用模块时遇到错误urllib,请在调用方法之前打开请求read()。
import urllib.request with urllib.request.urlopen('http://www.python.org/') as f: # 👇️ call read() here print(f.read())
开始调试的一个好方法是print(dir(your_object))查看字符串具有哪些属性。
这是打印 a 的属性的示例string。
my_string = 'hello world' # [ 'capitalize', 'casefold', 'center', 'count', 'encode', 'endswith', 'expandtabs', 'find', 'format', # 'format_map', 'index', 'isalnum', 'isalpha', 'isascii', 'isdecimal', 'isdigit', 'isidentifier', # 'islower', 'isnumeric', 'isprintable', 'isspace', 'istitle', 'isupper', 'join', 'ljust', 'lower', # 'lstrip', 'maketrans', 'partition', 'removeprefix', 'removesuffix', 'replace', 'rfind', 'rindex', # 'rjust', 'rpartition', 'rsplit', 'rstrip', 'split', 'splitlines', 'startswith', 'strip', 'swapcase', # 'title', 'translate', 'upper', 'zfill'] print(dir(my_string))
如果将一个类传递给dir()
函数,它会返回该类属性的名称列表,并递归地返回其基类的属性。
由于该str对象未实现read()方法,因此导致错误。
- AttributeError: ‘str’ 对象没有属性 ‘remove’
- AttributeError: ‘str’ 对象没有属性 ‘append’
- AttributeError: ‘str’ 对象没有属性 ‘decode’
- AttributeError: ‘str’ 对象没有属性 ‘get’ (Python)
- AttributeError: ‘str’ 对象没有属性 ‘strftime’
AttributeError: ‘str’ 对象没有属性 ‘remove’
当我们尝试remove()在字符串而不是列表上调用方法时,会出现 Python“AttributeError: ‘str’ object has no attribute ‘remove’”。
要解决该错误,请remove()在列表上调用该方法,或者
replace()在尝试从字符串中删除字符时使用该方法。
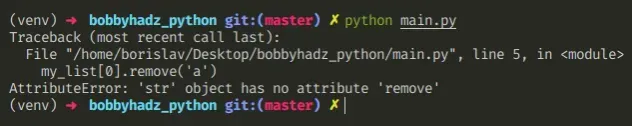
下面是错误如何发生的示例。
my_list = ['a', 'b', 'c'] # ⛔️ AttributeError: 'str' object has no attribute 'remove' my_list[0].remove('a')
0我们访问了索引(字符串)处的列表元素,并调用了remove()
导致错误的字符串的方法。
如果您需要从列表中删除一个项目,请调用remove()列表上的方法。
my_list = ['a', 'b', 'c'] my_list.remove('a') print(my_list) # 👉️ ['b', 'c']
list.remove ()方法从列表中删除第一项,其值等于传入的参数。
ValueError如果没有这样的项目,该方法将引发一个。
如果您需要处理在列表中找不到该项目的场景,请使用
try/except 语句。
my_list = ['a', 'b', 'c'] try: my_list.remove('r') except ValueError: print('Item not in list') print(my_list) # 👉️ ['a', 'b', 'c']
该remove()方法改变了原始列表并
返回 None。
如果您尝试从字符串中删除字符,请改用replace()方法。
my_str = 'apple banana kiwi' new_str = my_str.replace('banana', '') print(new_str) # 👉️ "apple kiwi"
通过用空字符串替换子字符串,我们有效地从字符串中删除了子字符串。
str.replace方法返回字符串的副本,其中所有出现的子字符串都被提供的替换项替换。
该方法采用以下参数:
| 姓名 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| 老的 | 字符串中我们要替换的子串 |
| 新的 | 每次出现的替换old |
| 数数 | count只替换第一次出现的(可选) |
这是打印 a 的属性的示例string。
my_string = 'hello world' # [ 'capitalize', 'casefold', 'center', 'count', 'encode', 'endswith', 'expandtabs', 'find', 'format', # 'format_map', 'index', 'isalnum', 'isalpha', 'isascii', 'isdecimal', 'isdigit', 'isidentifier', # 'islower', 'isnumeric', 'isprintable', 'isspace', 'istitle', 'isupper', 'join', 'ljust', 'lower', # 'lstrip', 'maketrans', 'partition', 'removeprefix', 'removesuffix', 'replace', 'rfind', 'rindex', # 'rjust', 'rpartition', 'rsplit', 'rstrip', 'split', 'splitlines', 'startswith', 'strip', 'swapcase', # 'title', 'translate', 'upper', 'zfill'] print(dir(my_string))
如果将一个类传递给dir()
函数,它会返回该类属性的名称列表,并递归地返回其基类的属性。
由于该str对象未实现remove()方法,因此导致错误。
如果您遇到以下任何错误,请单击与您相关的文章:
