NameError: name ‘ _ _ file _ _ ‘ is not defined’ in Python
‘NameError: name ‘__file__’ is not defined’ in Python
当我们在交互式 shell 中使用全局变量时,会发生“NameError: name ‘ _ _ file _ _ ‘ is not defined’”
。__file__
要解决该错误,请创建一个 Python 脚本并改为使用该命令运行该脚本
python script_name.py。
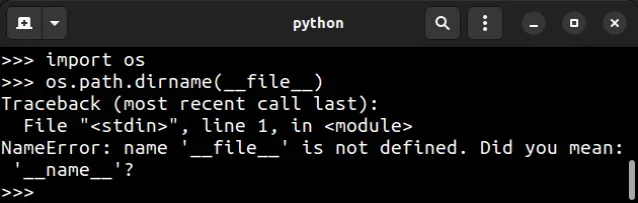
Traceback (most recent call last): File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module> NameError: name '__file__' is not defined. Did you mean: '__name__'?
__file__尝试在交互式 shell 中访问变量
最常见的错误原因是试图__file__在交互式 shell 中访问全局变量。
如果您需要在交互式 shell 中访问变量,请尝试以下代码示例。
import os # 👇️ '/home/borislav/Desktop/bobbyhadz_python' os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath('__file__'))
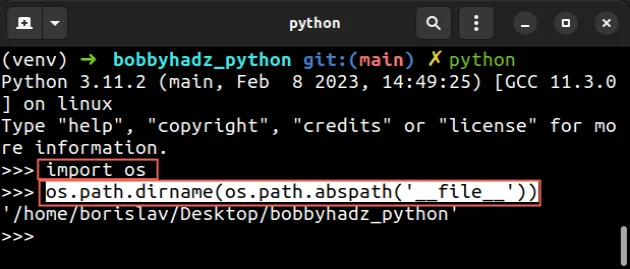
该os.path.abspath方法采用路径并返回路径的规范化绝对版本。
将代码存储在 Python 模块中
但是,更好的方法是将代码存储在 Python 模块中。
创建一个名为的文件main.py并将以下代码添加到文件中。
import os result = os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__)) # 👇️ /home/borislav/Desktop/bobbyhadz_python print(result)
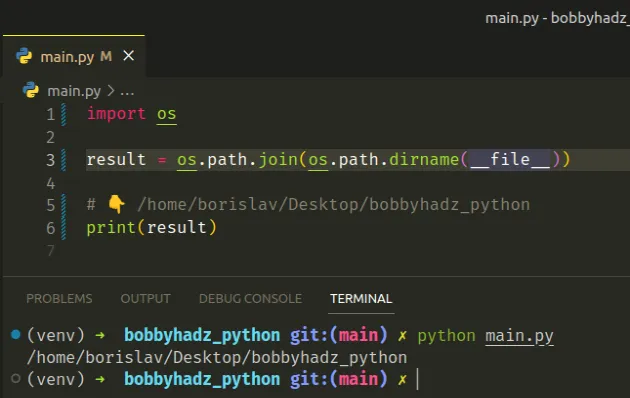
现在您可以使用命令python main.py而不是使用交互式 shell 来运行您的代码。
您可以使用该函数退出交互式 shell exit()。
exit()
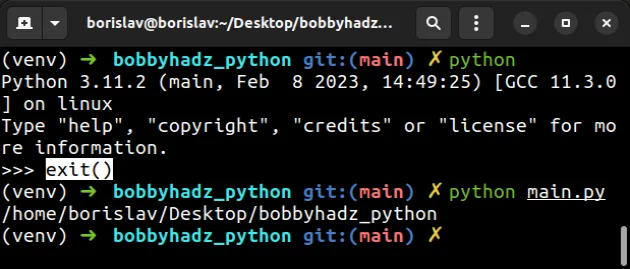
现在使用命令运行您的 Python 模块python main.py。
python main.py # 👇️ for Python 3 python3 main.py # 👇️ using py alias (Windows) py main.py
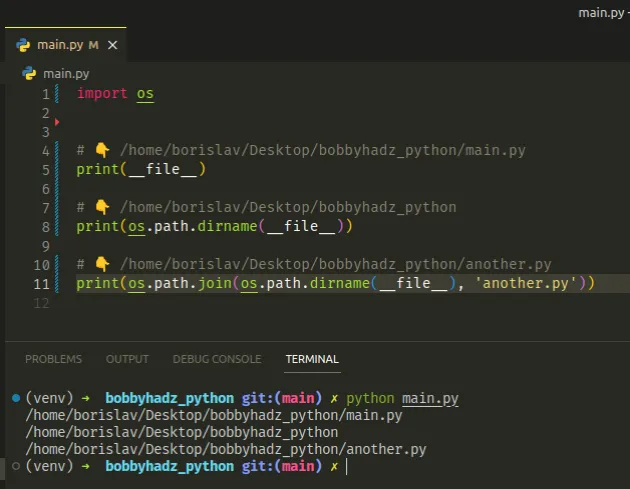
当你在 Python 中加载一个模块时,全局__file__变量被设置为其路径。
import os # 👇️ /home/borislav/Desktop/bobbyhadz_python/main.py print(__file__) # 👇️ /home/borislav/Desktop/bobbyhadz_python print(os.path.dirname(__file__)) # 👇️ /home/borislav/Desktop/bobbyhadz_python/another.py print(os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__), 'another.py'))
The
os.path.dirname
method returns the directory component of a pathname.
The
os.path.join
method joins one or more paths intelligently.
import os # 👇️ /home/bobbyhadz print(os.path.join('/', 'home', 'bobbyhadz'))
The method concatenates the provided paths with exactly one directory separator
following each non-empty part except the last.
If any of the provided components is an absolute path, all previous components
are thrown away and joining continues from the absolute path onwards.
# Using the inspect module instead
An alternative approach is to use the inspect module to get the path to the
current file.
import inspect file_path = inspect.getfile(lambda: None) # 👇️ /home/borislav/Desktop/bobbyhadz_python/main.py print(file_path)
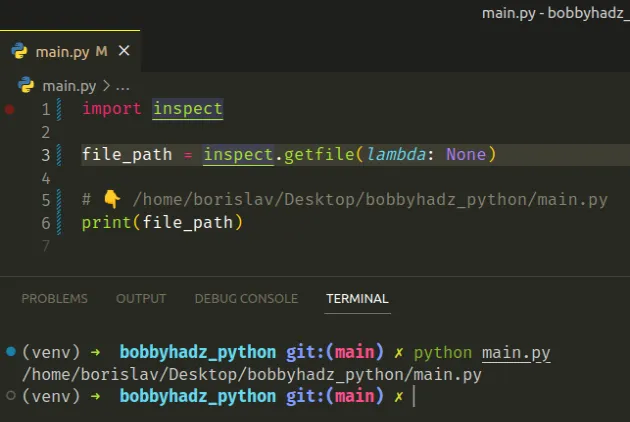
The inspect.getfile() method returns the absolute path to the module in which
the lambda function is defined.
In other words, it returns the absolute path to the current module.
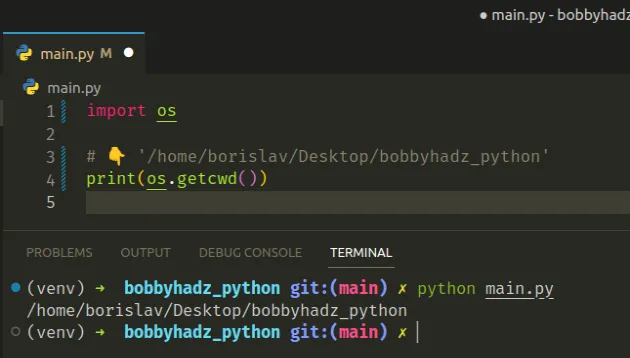
# Getting the current working directory with os.getcwd()
You can use the os.getcwd
method if you need to get the current working directory.
import os # 👇️ '/home/borislav/Desktop/bobbyhadz_python' print(os.getcwd())
# Getting the name of the module with sys.argv
If you need just the name of the current module, use the sys.argv list.
import sys print(sys.argv[0]) # 👉️ main.py
The sys.argv list
contains the command line arguments that were passed to the Python script.
argv[0] is the name of the script, argv[1] is the first provided command line argument, etc.# Accessing the attribute on imported modules
The __file__ attribute is also available on modules you import into your
Python script (e.g. main.py).
例如,这里有一个名为another.py导入main模块并使用其__file__属性的文件。
import main # 👇️ /home/borislav/Desktop/bobbyhadz_python/main.py print(main.__file__)
另一个例子是安装第三方模块。
pip install transformers pip3 install transformers
现在我可以导入transformers
模块并访问它的__file__属性以获取存储模块的文件的路径。
import transformers # 👇️ /home/borislav/Desktop/bobbyhadz_python/venv/lib/python3.10/site-packages/transformers/__init__.py print(transformers.__file__)
