NameError: 名称 ‘operator’ 未在 Python 中定义
NameError: name ‘operator’ is not defined in Python
Python“NameError: name ‘operator’ is not defined”发生在我们使用
operator模块而不先导入它时。要解决错误,请
operator在使用之前导入模块 – import operator。
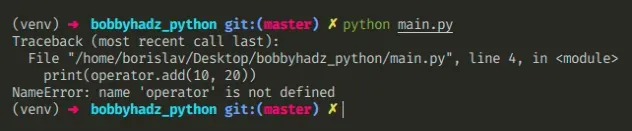
下面是错误如何发生的示例。
# ⛔️ NameError: name 'operator' is not defined print(operator.add(10, 20))
我们必须导入
operator模块来解决错误。
# ✅ import operator module first import operator print(operator.add(10, 20)) # 👉️ 30
即使该operator模块在 Python 标准库中,我们仍然需要在使用前导入它。
o when importing operator because module names are case-sensitive.Also, make sure you haven’t imported operator in a nested scope, e.g. a
function. Import the module at the top level to be able to use it throughout
your code.
An alternative to importing the entire operator module is to import only the
functions that your code uses.
from operator import add, sub print(add(10, 20)) # 👉️ 30 print(sub(20, 10)) # 👉️ 10
The example shows how to import only the add and sub functions from the
operator module.
Instead of accessing the members on the module, e.g. operator.add, we now
access them directly.
This should be your preferred approach because it makes your code easier to
read.
import operator, it is much harder to see which functions from the operator module are being used in the file.Conversely, when we import specific functions, it is much easier to see which
functions from the operator module are being used.
You can view all of the functions the operator module provides by visiting the
official docs.
Conclusion #
The Python “NameError: name ‘operator’ is not defined” occurs when we use the
operator module without importing it first. To solve the error, import the
operator module before using it – import operator.