NameError:名称“reduce”未在 Python 中定义
NameError: name ‘reduce’ is not defined in Python
Python“NameError: name ‘reduce’ is not defined”发生在我们使用该
reduce()函数而不先导入它时。functools要解决该错误,请在使用之前
从模块中导入函数- from functools import reduce。
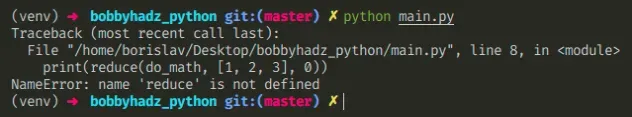
下面是错误如何发生的示例。
def do_math(accumulator, current): return accumulator + current # ⛔️ NameError: name 'reduce' is not defined print(reduce(do_math, [1, 2, 3], 0)) # 👉️ 6
为了解决这个错误,我们必须从
模块中导入reduce函数。functools
from functools import reduce def do_math(accumulator, current): return accumulator + current print(reduce(do_math, [1, 2, 3], 0)) # 👉️ 6
reduce
函数采用以下 3 个参数:
| 姓名 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| 功能 | 一个带有 2 个参数的函数 – 累加值和可迭代的值。 |
| 可迭代的 | iterable 中的每个元素都将作为参数传递给函数。 |
| 初始值设定项 | 一个可选的初始化值,在计算中放置在可迭代项之前。 |
你会经常看到reduce()函数被传递了一个lambda:
from functools import reduce # 👇️ 6 print( reduce( lambda accumulator, current: accumulator + current, [1, 2, 3], 0 ) )
例子中的lambda函数以累计值和当前值作为参数,返回两者之和。
如果我们为参数提供一个值initializer,它会被放在计算中可迭代项的前面。
from functools import reduce def do_math(accumulator, current): print(accumulator) # 👉️ is 0 on first iteration return accumulator + current # 👇️ 6 print( reduce( do_math, [1, 2, 3], 0 # 👈️ initializer set to 0 ) )
在示例中,我们传递0了初始化参数,因此 的值
accumulator将出现0在第一次迭代中。
The value of the accumulator would get set to the first element in the
iterable if we didn’t pass a value for the initializer.
def do_math(accumulator, current): print(accumulator) # 👉️ is 1 on first iteration return accumulator + current # 👇️ 6 print( reduce( do_math, [1, 2, 3], ) )
If the iterable is empty and the initializer is provided, the initializer
is returned.
from functools import reduce def do_math(accumulator, current): return accumulator + current # 👇️ 100 print( reduce( do_math, [], 100 # 👈️ initializer set to 100 ) )
If the initializer is not provided and the iterable contains only 1 item,
the first item is returned.
from functools import reduce def do_math(accumulator, current): return accumulator + current # 👇️ 123 print( reduce( do_math, [123], ) )
The list in the example only contains a single element and we didn’t provide a
value for the initializer, so the reduce() function returned the list
element.
Conclusion #
The Python “NameError: name ‘reduce’ is not defined” occurs when we use the
reduce() function without importing it first. To solve the error, import the
function from the functools module before using it –
from functools import reduce.
