目录
Using user input to select an option from a list in Python
在 Python 中使用用户输入从列表中选择一个选项
要使用用户输入从列表中选择一个选项:
- 构建包含选项的消息。
- 使用
input()函数获取用户输入。 - 检查用户是否输入了可能的选项之一。
options = ['python', 'js', 'ts'] user_input = '' input_message = "Pick an option:\n" for index, item in enumerate(options): input_message += f'{index+1}) {item}\n' input_message += 'Your choice: ' while user_input.lower() not in options: user_input = input(input_message) print('You picked: ' + user_input)
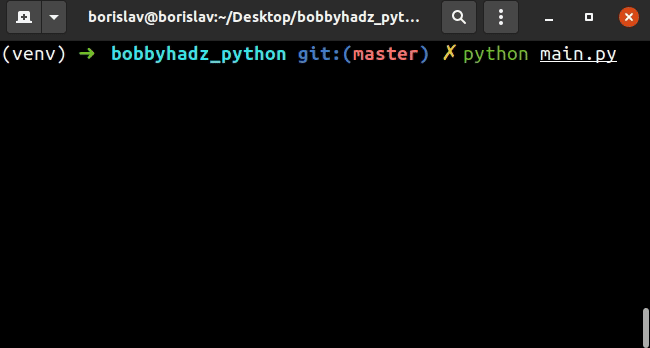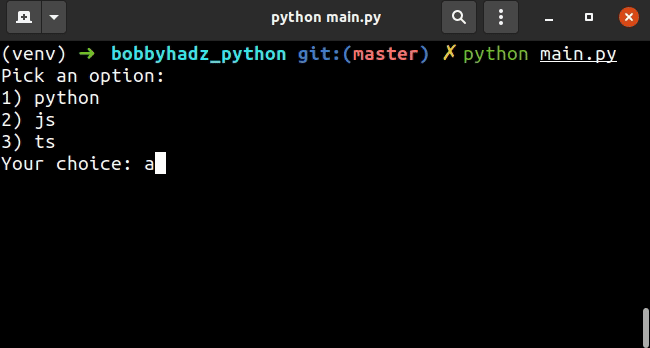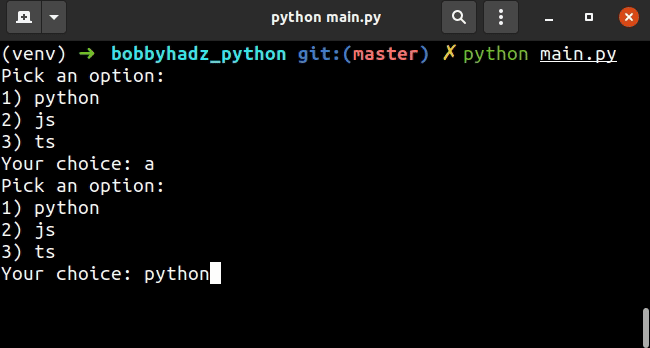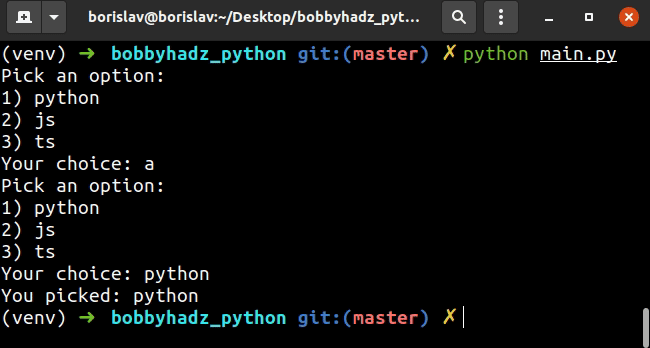
该示例让用户选择列表中的选项之一。
python, , ,但您也可以调整它并让用户键入与列表项相对应的数字。 jstsoptions = ['python', 'js', 'ts'] user_input = '' input_message = "Pick an option:\n" for index, item in enumerate(options): input_message += f'{index+1}) {item}\n' input_message += 'Your choice: ' while user_input not in map(str, range(1, len(options) + 1)): user_input = input(input_message) print('You picked: ' + options[int(user_input) - 1])
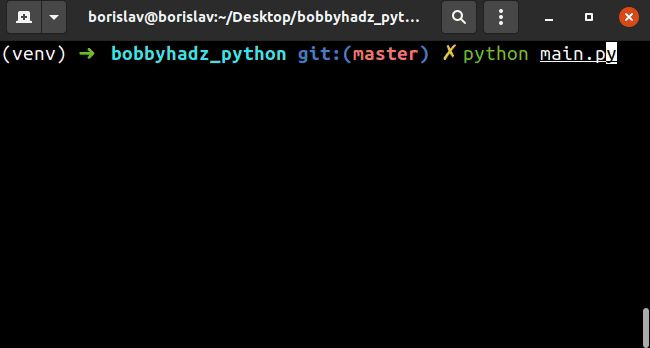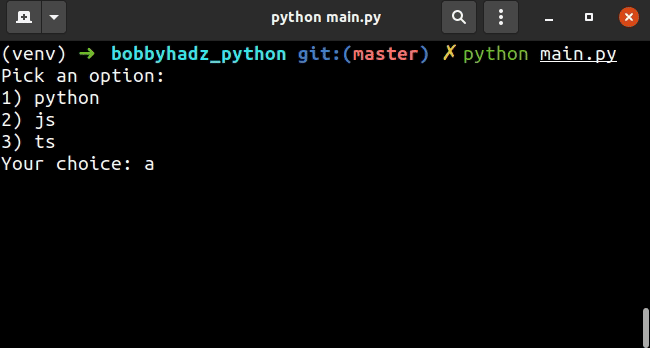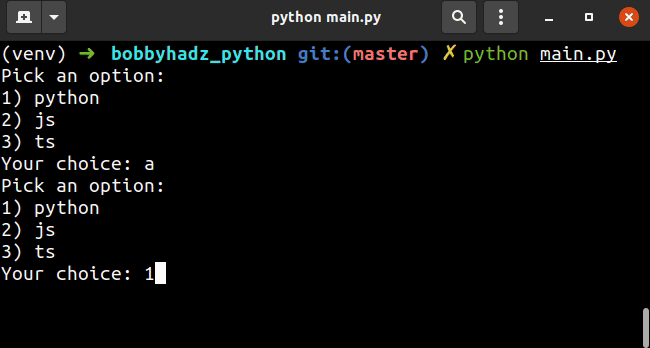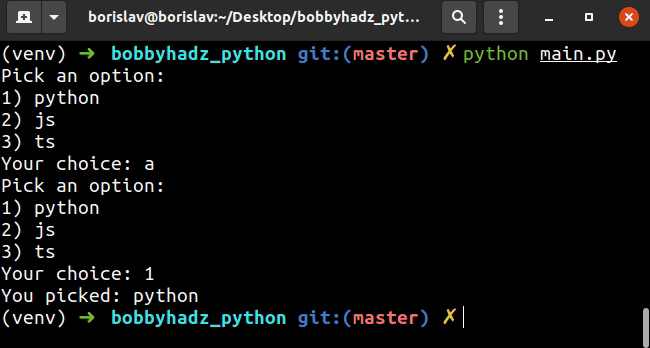
上面的代码片段希望用户输入一个与列表项相对应的数字。
我们使用
格式化的字符串文字来构造输入消息。
格式化字符串文字 (f-strings) 让我们通过在字符串前加上f.
my_str = 'is subscribed:' my_bool = True result = f'{my_str} {my_bool}' print(result) # 👉️ is subscribed: True
确保将表达式括在大括号 – 中{expression}。
enumerate函数接受一个可迭代对象并返回一个包含元组的枚举对象,其中第一个元素是索引,第二个是项目。
my_list = ['apple', 'banana', 'melon'] for index, item in enumerate(my_list): print(index, item) # 👉️ 0 apple, 1 banana, 2 melon
在每次迭代中,我们添加1到索引以使选项从1.
options = ['python', 'js', 'ts'] user_input = '' input_message = "Pick an option:\n" for index, item in enumerate(options): input_message += f'{index+1}) {item}\n' input_message += 'Your choice: ' while user_input not in map(str, range(1, len(options) + 1)): user_input = input(input_message) print('You picked: ' + options[int(user_input) - 1])
while循环来不断迭代,直到选择的选项是列表中的值之一或相应的数字之一。一旦用户选择了一个有效选项,条件不再满足,我们退出循环while。
这是另一个例子。
Python 用户输入的多项选择题
要使用用户输入定义多项选择题:
- 使用
input()函数从用户那里获取输入。 - 检查输入是否是指定选项之一。
- 使用条件语句检查输入是否是可用选项之一。
user_input = '' while True: user_input = input( 'Pick one: 1) Python | 2) JavaScript | 3) TypeScript [1/2/3]? ') if user_input == '1': print('You picked Python') break elif user_input == '2': print('You picked JavaScript') break elif user_input == '3': print('You picked TypeScript') break else: print('Type a number 1-3') continue
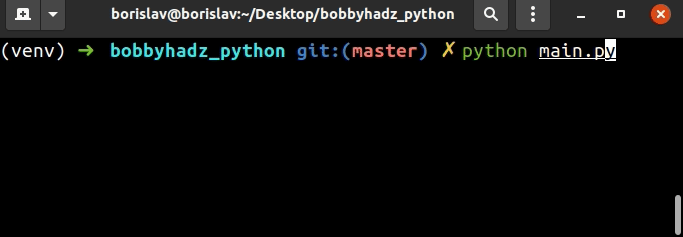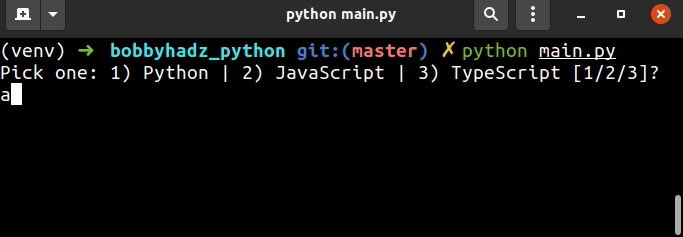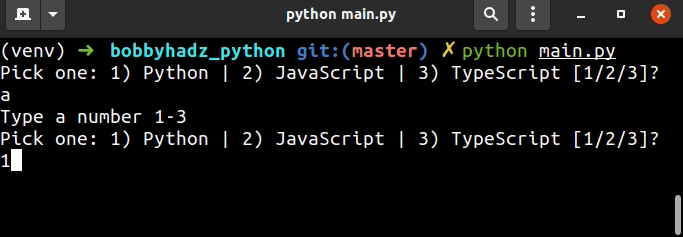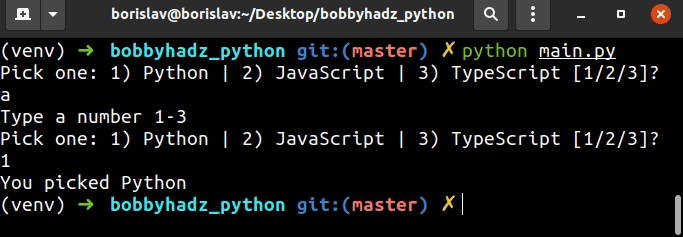
我们使用while True循环进行迭代,直到用户输入其中一个选项。
while True是使用语句。 breakbreak语句跳出最内层的for 或 while循环。
continue 语句继续
循环的下一次迭代。
该continue语句用于在用户输入错误选项时再次提示用户。
输入函数接受一个可选参数并将其写入标准输出而prompt
没有尾随换行符。
input()函数始终保证返回一个字符串,即使用户输入了一个数字。您也可以使用字母作为选项。
user_input = '' while True: user_input = input( 'Pick one: A) Python | B) JavaScript | C) TypeScript [A/B/C]? ') if user_input.upper() == 'A': print('You picked Python') break elif user_input.upper() == 'B': print('You picked JavaScript') break elif user_input.upper() == 'C': print('You picked TypeScript') break else: print('Type a letter A-C') continue
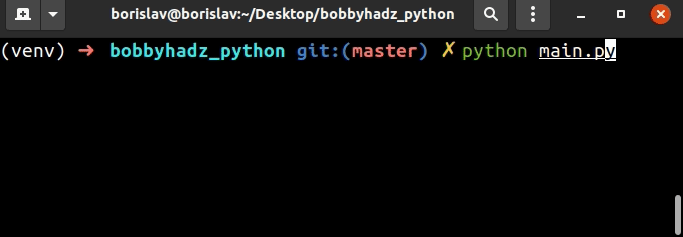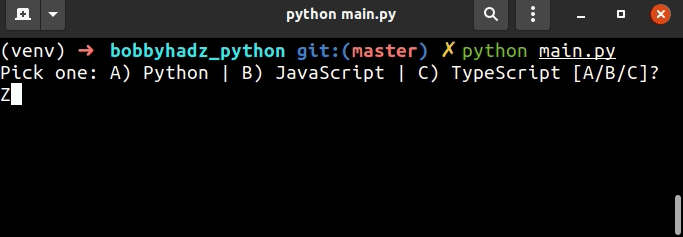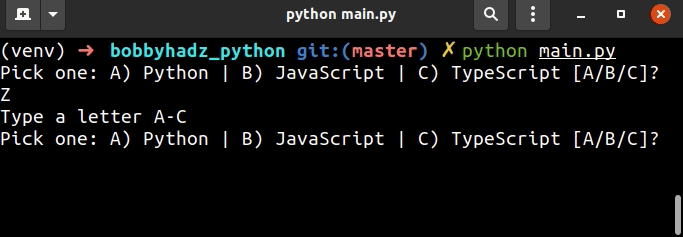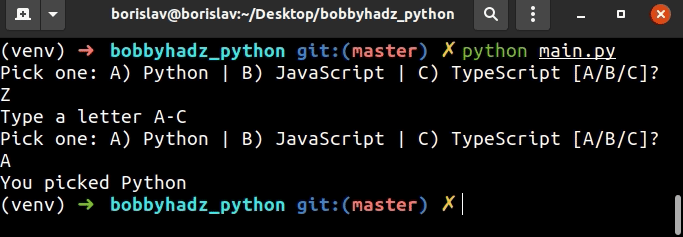
代码片段提示用户从多个可用选项中选择一个,但使用字母而不是数字。
我们使用该str.upper()方法将输入值大写,因此即使用户输入a,b或 也满足条件c。
str.upper
方法返回字符串的副本,其中所有大小写字符都转换为大写。
print('a'.upper()) # 👉️ 'A' print('z'.upper()) # 👉️ 'Z'
一旦用户输入了有效的选项,我们就使用该break语句跳出循环while。
使用 inquirer 包通过用户输入选择一个选项
或者,您可以使用
inquirer包。
在项目的根目录中打开终端并安装inquirer.
pip install inquirer
现在我们可以导入并使用这个inquirer包了。
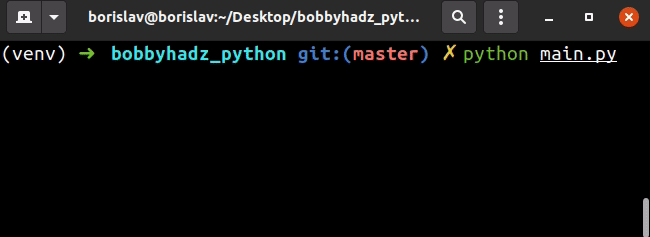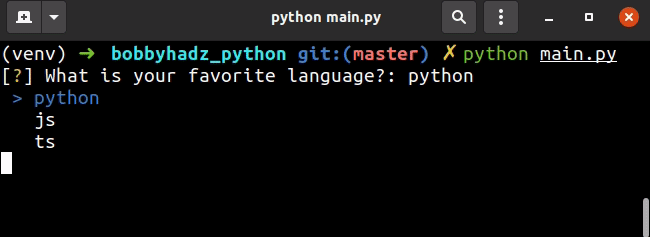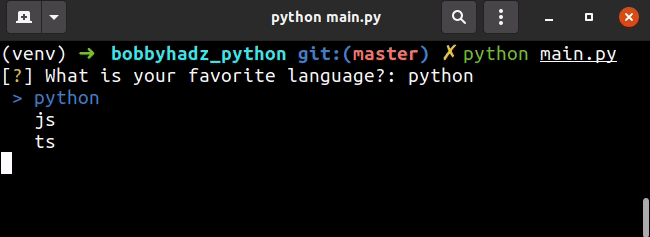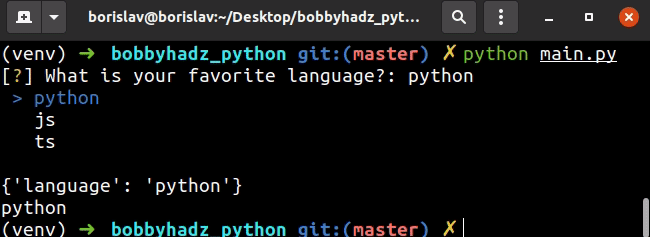
import inquirer options = ['python', 'js', 'ts'] questions = [ inquirer.List('language', message="What is your favorite language?", choices=options, ), ] answers = inquirer.prompt(questions) print(answers) print(answers['language'])
您可以使用键盘上的箭头键选择其中一个选项。
请注意,inquirer包主要用于基于 Unix 的平台(Linux 和 MacOS)。
该软件包具有对 Windows 的实验性支持。
额外资源
您可以通过查看以下教程来了解有关相关主题的更多信息:
- 是/否关于 Python 中用户输入的问题
- 如何在 Python 中将用户输入保存到文件中
- 如何在 Python 中获取整数用户输入
- 在 Python 中使用用户输入从列表中选择一个选项
- 在 Python 中获取用户输入的布尔值(真/假)
- 如何在 Python 中根据用户输入创建日期
- 从 Python 中的用户输入获取文件路径
- 如何在 Python 中获取 Float 用户输入
- Python 中的多行用户输入
- 在 Python 中只接受来自用户输入的单个字符
- 在 Python 中根据用户输入创建元组或集合
- 如何在 Python 中验证用户输入
- 在 Python 中使用 For 或 While 循环获取用户输入
- 如何在 Python 中检查用户输入是否为空
- 如何在 Python 中将用户输入添加到字典
- 如何从 Python 中的用户输入中获取列表
