在 React 中从状态数组中删除一个对象
Remove an Object from state Array in React
在 React 中从状态数组中移除一个对象:
- 使用该
filter()方法遍历数组。 - 在每次迭代中,检查是否满足条件。
- 将状态设置为
filter方法返回的新数组。
应用程序.js
import {useState} from 'react'; export default function App() { const initialState = [ {id: 1, name: 'Alice', country: 'Austria'}, {id: 2, name: 'Bob', country: 'Belgium'}, ]; const [employees, setEmployees] = useState(initialState); const removeSecond = () => { setEmployees(current => current.filter(employee => { // 👇️ remove object that has id equal to 2 return employee.id !== 2; }), ); }; return ( <div> <button onClick={removeSecond}>Remove second</button> {employees.map(({id, name, country}) => { return ( <div key={id}> <h2>name: {name}</h2> <h2>country: {country}</h2> <hr /> </div> ); })} </div> ); }
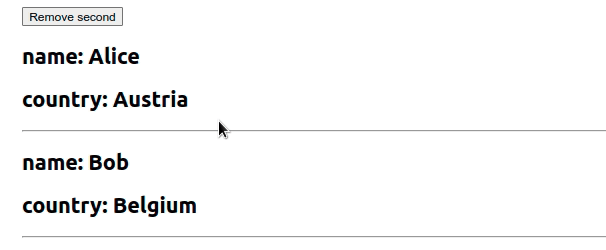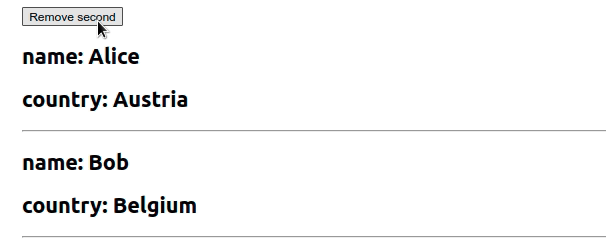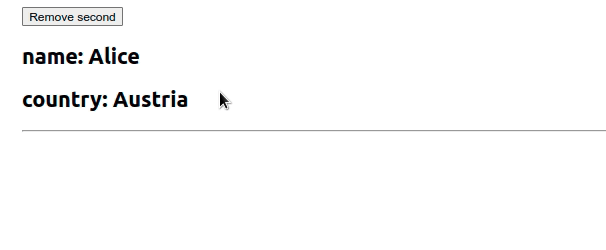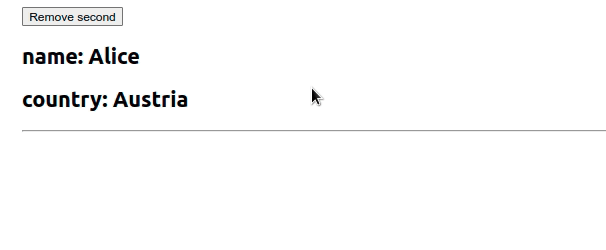
我们使用useState钩子初始化了一个employees状态变量
。
我们传递给
Array.filter
方法的函数将针对数组中的每个元素进行调用。
在每次迭代中,我们检查id对象的属性是否不等于
2并返回结果。
应用程序.js
const initialState = [ {id: 1, name: 'Alice', country: 'Austria'}, {id: 2, name: 'Bob', country: 'Belgium'}, ]; const filtered = initialState.filter(obj => { // 👇️ returns truthy for all elements that // don't have an id equal to 2 return obj.id !== 2; }); // 👇️ [{id: 1, name: 'Alice', country: 'Austria'}] console.log(filtered);
该filter方法返回一个新数组,其中仅包含回调函数返回真值的元素。
如果从未满足条件,则该
Array.filter函数返回一个空数组。我们将一个函数传递给setState,因为该函数保证以当前(最新)状态调用。
应用程序.js
const removeSecond = () => { // 👇️ current is the current state array setEmployees(current => current.filter(employee => { return employee.id !== 2; }), ); };
当使用前一个状态计算下一个状态时,将一个函数传递给
setState.
否则,如果我们有权访问的状态数组不代表最新值,我们可能会遇到一些奇怪的竞争条件。
如果您需要根据多个条件从状态数组中删除一个对象,请使用
逻辑与 (&&)
或
逻辑或 (||)
运算符。
应用程序.js
const initialState = [ {id: 1, name: 'Alice', country: 'Austria'}, {id: 2, name: 'Bob', country: 'Belgium'}, {id: 3, name: 'Carl', country: 'Austria'}, ]; const [employees, setEmployees] = useState(initialState); const remove = () => { setEmployees(current => current.filter(employee => { return employee.id !== 3 && employee.id !== 2; }), ); };
我们使用了逻辑与 (&&) 运算符,如果两个条件都满足,它只会返回一个真值。
true仅当id对象的属性不等于3且不等于时,回调函数才返回2。
这是一个使用逻辑或 (||) 运算符的示例。
应用程序.js
const initialState = [ {id: 1, name: 'Alice', country: 'Austria'}, {id: 2, name: 'Bob', country: 'Belgium'}, {id: 3, name: 'Carl', country: 'Austria'}, ]; const [employees, setEmployees] = useState(initialState); const remove = () => { setEmployees(current => current.filter(employee => { return employee.name === 'Alice' || employee.name === 'Carl'; }), ); };
两个条件中的任何一个都必须评估为要添加到新数组的元素的真值。
换句话说,如果name对象上的属性等于Alice或等于Carl,则该对象将被添加到新数组中。所有其他对象都从数组中过滤掉。
